New Audit Reveals Denver Is Delivering Fewer Units Than Required, Costs Climb For Taxpayer-Funded Affordable Housing
by Glen Richardson
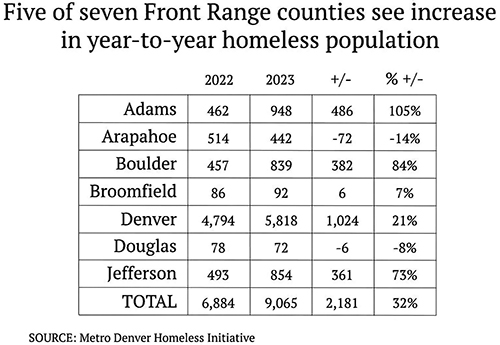
As 2024 begins, residents want to know if Mayor Mike Johnston met his $50 million promise to move 1,000 of Denver’s homeless off the streets by year’s end. Many others — like Councilmember Stacie Gilmore, who resigned as homeless committee chair — have concluded the administration’s homeless pledge is nothing more than “a dog and pony show.”
Facing the facts: Denver has the nation’s 10th-most homeless people. At year’s end there were 802 homeless people getting monthly payments of from $50 to $1,000. One group receives $1,000 a month for 12 months; another received a $6,500 lump payment and then $500 a month for 11 months; and the final group receives $50 a month for a year. For this year (2024), Mayor Johnston proposes to spend $242 million on homeless-affordable housing.

Street Sweep Scene: Denver continues to perform “sweeps” of homeless encampments under new Denver Mayor Mike Johnston. Photo: Kevin J. Beaty
A new financial examination by Denver Auditor Timothy M. O’Brien, however, reveals that finding housing or giving out money — without managing inherent and built-in factors — may b

Street Squalor Struggle: Despite providing money, plus developing and prioritizing affordable housing projects, Denver’s homeless crisis continues to surge as 2024 begins. Photo (left): Hart Van Denburg/CPR
e an emotional feat, but won’t accomplish the city’s objectives.
Unit Count Con
The audit’s most glaring discovery: Denver’s Department of Housing Stability is not delivering the required number of units. Fact: Denver developed 32 fewer units for very-low income and 301 fewer for moderate-income households than required by the city agreement.
Equally disturbing: The agency reported 203 units for rent at “market rates,” claiming they count as part of the agreement to develop affordable housing.
Lack of oversight is to blame, according to Auditor O’Brien. “If affordable housing is a priority, leaders need to effectively use resources, show accountability for housing goals, and commitment to helping those in Denver who need it m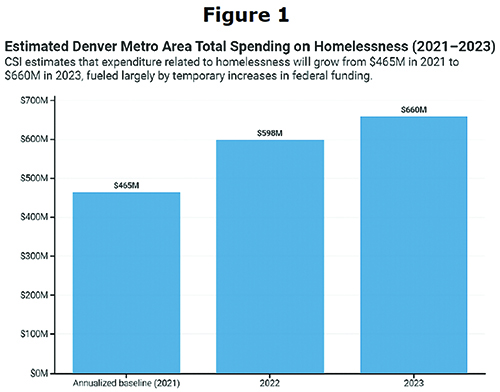 ost,” he asserts.
ost,” he asserts.
Shoddy Upkeep
Auditors also found a lack of oversight to maintain safe-habitable housing units for people in the lowest income ranges. Not only are these people subject to health-safety risks, but the city could lose part of its affordable housing inventory due to damage and disrepair.
A random check of 20 affordable housing projects funded by the Department of Housing Stability — plus an affordable housing project used as permanent housing and funded with program funds — examiners found building doors unlocked or propped open; doors missing handles; water damage; pet or human waste in public areas; plus, trash and debris.
More: Broken windows; dirty or damaged carpets; potential fire code violations, which were reported to the fire department; large cracks and other damage to exterior brick or foundations; evidence of pest infestations; exposed electrical wires or damaged electrical features; window and screens missing or damaged; inoperable or malfunctioning elevators; standing water in public areas; and damaged interior and exterior lighting.
Fewer New Units
Even more troubling, auditors found plans for new units are falling below requirements in the city’s taxpayer-funded agreement with the Denver Housing Authority. Denver partners with the Denver Housing Authority on their “DHA Delivers for Denver Program” — commonly called “D3.”

Broadway’s Best: Purchased by the Denver Housing Authority and completed in 2022, this 655 Broadway Bldg. rents to income limited elderly and disabled.
The audit discovered the housing authority reported some units were being rented at market rate, instead of at affordable rates for people with low-income levels.
Moreover, the housing authority also developed fewer units for low-and moderate-income individuals than required. Bottom line: Investments may and many times exceed what was agreed upon. There is no clarity on how many housing units will be delivered or if the units will be affordable for people who need it most. “The city needs stronger oversight to confirm the affordable housing results it promises,” says Auditor O’Brien. “It’s clear the city is too trusting in third-party partners and as a result the people who need the most help could be left out.”
Half Have High Rent
Just as shocking and upsetting, the audit reveals that half of the units in the city’s D3 agreement exceed the rents allowed by that agreement.
The housing authority reported 203 market-rate units paid for by the city’s D3 agreement were rented for between 60% and 90% of area median income. The housing authority claims this counts toward contract requirements because they are lower than the average rental prices in Denver, which are about 120% of the area median income.
While about half of these ar

Loose Connections: Audits of 20 affordable housing projects funded by the Department of Housing Stability found shoddy upkeep, including exposed-damaged electrical wires.
e rented at rates for people in the target income, the lower-than-average prices are not guaranteed if market conditions change — resulting in potential rent increases and loss of affordability.
District Deals
Additionally, some City Council districts are receiving more affordable housing resources than allowed. Specifically, districts 1, 3, 8, and 9 all received more affordable housing funds than allowed.
Further, district 3 was restricted to receiving fewer funds than other districts because of existing affordable housing investments. While the agreement allows the department to grant a waiver to any one district, except district 3, discussions about waivers are ongoing.
The housing authority is also counting units developed with “different city funding sources” as part of the D3 project, further inflating the results.
Clinch & Confirm
Finally, the audit found several other areas in which the city can make improvements to maintain and improve the city’s affordable housing struggle.
First, the city is not ensuring contractors are complying with wage laws on affordable housing projects. These projects may be subject to federal wage requirements or the city’s prevailing wage ordinance.
The Department of Housing Stability also needs to verify income annually for residents. The department also needs adequate
controls over its data, including what is used to populate public dashboards.
The Department of Housing Stability has agreed to implement nearly 90% (17 of the 19) of the audit recommendations.
It is disappointing, however, that the department chose to disagree with two of the audit recommendations. Those proposals would significantly improve the city’s inspection and maintenance of homeless units. Furthermore, it would ensure affordable housing is sanitary and safe.
The audit found issues at 14 of 21 homeless properties, despite inspection forms from the city showing no issues at the same properties.